What are the treatments?
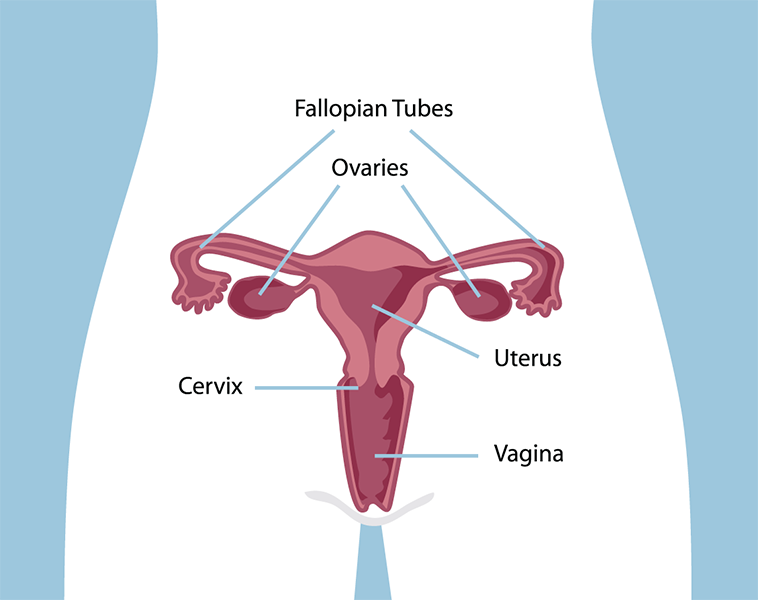
Conservative treatments for pre-cancerous conditions of the cervix include “Cryotherupy”, which destroys the abnormal cells by freezing, and “carbon dioxide laser cautery”, where a very fine, precise beam of focused light burns the abnormal cells. These procedures are performed using a local anesthetic, usually cause only minor discomfort, and take less than 5 minutes.
“Cone biopsy” is a minor surgical procedure which removes abnormal tissue extending into the opening of the cervix.
These treatments are simple, almost always successful in curing the abnormality, and should not affect the woman’s fertility or future child-bearing.